
Contact Us

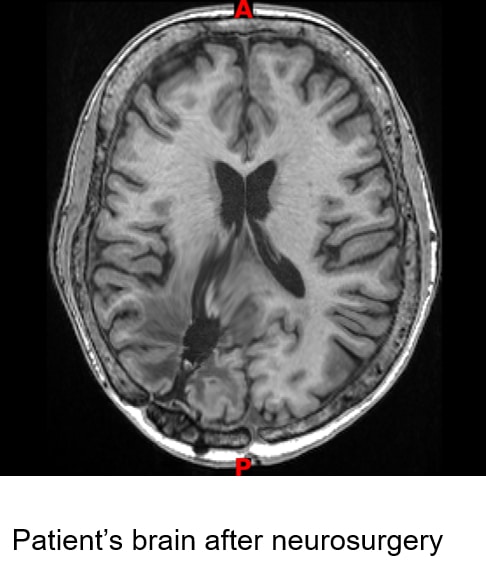
At Neurotherapeutix in New York City, we offer a specialized approach to treating neurological sequelae that occur after neurosurgery.
Using functional MRI-guided transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), we help clients recover cognitive, sensory, and motor function through personalized, non-invasive therapy.
If you’re experiencing ongoing symptoms after brain or spinal surgery, our innovative neurorehabilitation process supports recovery and improves quality of life.
Continue reading to learn how our guided TMS therapy works.
“Sequelae” refers to the residual neurological symptoms or deficits that persist after neurosurgical procedures.
These complications can result from damage to specific brain regions during surgery or the body’s post-surgical healing response.
While neurosurgery is often necessary to address life-threatening neurological conditions, it can unintentionally impair cognitive, sensory, or motor pathways.
If you have sequelae, you may experience:
Post-operative deficits may result from:
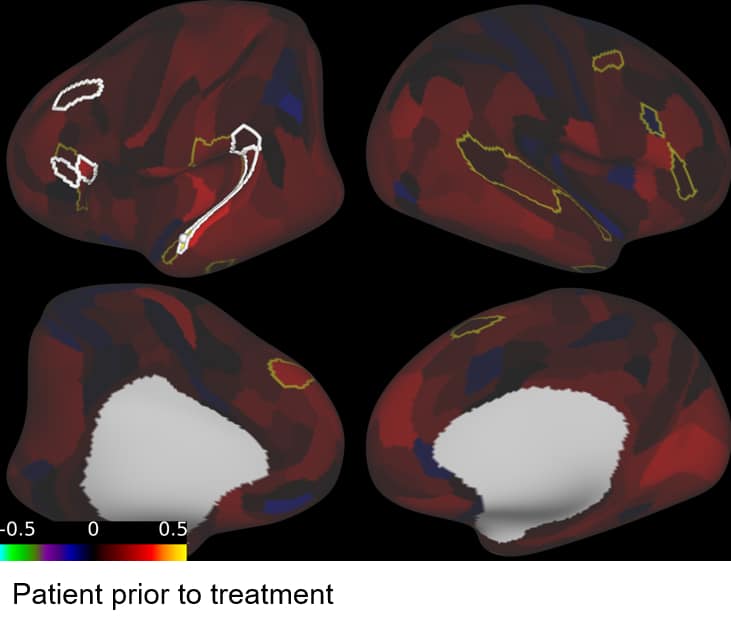
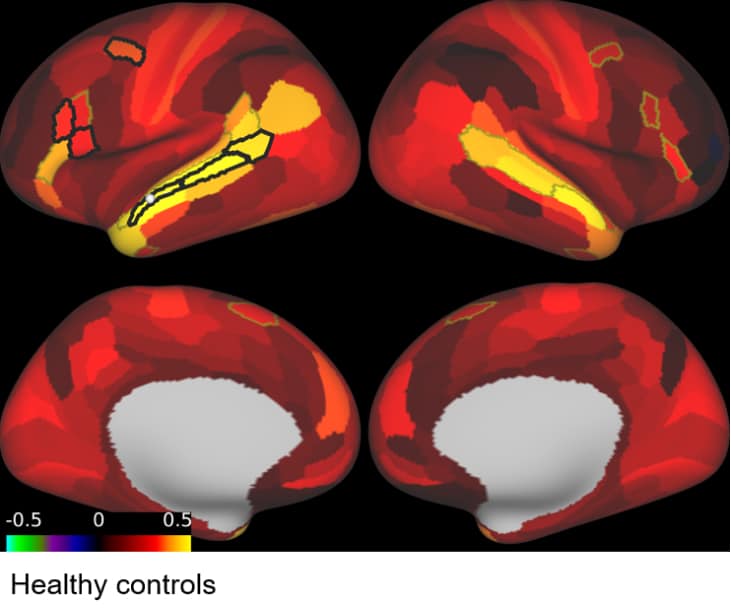
At Neurotherapeutix, we’ve developed neuromodulation-based rehabilitation (NBR). This approach uses resting-state functional MRI (rsfMRI) to guide targeted TMS sessions that stimulate disrupted brain networks.
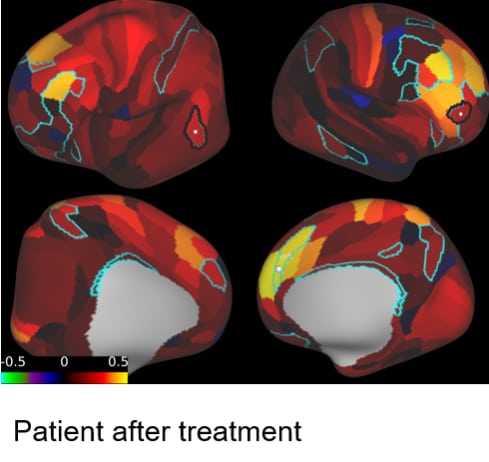
Unlike conventional rehabilitation, which relies on slow, general recovery, NBR actively promotes cortical reorganization and functional brain recovery in weeks instead of months.
Guided TMS therapy can:
TMS therapy is especially beneficial when standard rehabilitation methods yield limited results. It is safe, pain-free, and personalized using real-time brain data.
Our guided TMS therapy follows a structured, personalized process that allows us to target the brain regions most affected by neurosurgical intervention.
Here’s what you can expect during your treatment:
You may be a candidate for guided TMS therapy if you:
We work with individuals recovering from brain tumor resection, trauma-related surgery, epilepsy surgery, and other neurosurgical procedures.
Neurotherapeutix is a trusted leader in brain imaging and neuromodulation.
Our personalized treatment model helps clients overcome the lingering effects of neurosurgery through science-backed, non-invasive care.
If you or a loved one is struggling with post-surgical deficits, we’re here to help you explore how fMRI-guided TMS therapy can support your recovery.
Request an appointment or contact our Upper East Side clinic to get started.


Call us at (917) 388-3090 or click to request a regular or telehealth appointment.
Neurotherapeutix
171 East 74th Street, Unit 1-1 New York, NY 10021

Neurotherapeutix is the leading clinic for functional imaging guided transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), a safe, innovative, and non-invasive methodology for treating a wide range of acute and chronic mental disorders and brain injuries. Our advanced fMRI technology allows us to map the brain for the… Learn More »
By: Neurotherapeutix NYC
Reviewed By: Marta Moreno, Ph.D
Published: March 24, 2023
Last Reviewed: September 27, 2024
QUICK INQUIRY
Contact us to get an estimate for your medical services requirements. You can fill in the form to specify your medical requirements or you can call us directly.