If you’re exploring transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) therapy, it’s natural to wonder whether insurance will help cover the cost.
Insurance coverage for TMS can be complex and depends on factors such as diagnosis, treatment history, insurance provider, and the specific type of TMS being considered.
In some cases, insurance may cover TMS therapy. Coverage decisions are typically made on a case-by-case basis and guided by insurer-specific criteria, and approval is never guaranteed.
Understanding how these decisions are made can help you feel more prepared as you explore treatment options for mental health or neurological conditions.
When insurance may cover TMS
Insurance providers rely on defined clinical criteria when evaluating whether TMS qualifies for coverage. These criteria vary by insurer and plan.
Medical necessity and diagnosis requirements
When insurance coverage is approved, it is typically tied to documentation showing that TMS is medically necessary for a specific condition. One commonly cited example in insurance policies is major depressive disorder (MDD), particularly when symptoms are persistent or severe.
That said, coverage guidelines differ widely. Some insurance plans are narrowly defined, while others allow broader interpretation based on clinical documentation and medical review.
Coverage decisions are made by the insurer, not the treating clinic.
Prior treatment history
Insurance approval for TMS often depends on prior treatment history. This may include documentation showing that other standard treatments, such as medication or psychotherapy, did not provide sufficient symptom improvement or were not well tolerated.
The number and type of treatments required before TMS therapy can vary significantly between insurance providers.
Common insurance providers and TMS coverage
Coverage policies vary by insurance plan.
Private insurance
Some private insurance plans may cover standard TMS therapy when specific diagnostic and treatment history requirements are met. Prior authorization is typically required, and coverage rules can vary even within the same insurance company.
Approval depends on how closely the proposed treatment aligns with the insurer’s established coverage criteria.
Medicare and Medicaid
Medicare may provide coverage for TMS therapy under certain circumstances when medical necessity requirements are met. Medicaid coverage varies by state and is often more limited.
Because insurance policies change over time, it’s essential to verify coverage details directly with your insurance provider.
Why coverage varies by clinic and technology
Insurance coverage for TMS is influenced not only by diagnosis, but also by how treatment is delivered.
Standard vs. advanced fMRI-guided TMS
Most insurance policies are structured around standard TMS protocols, which use generalized stimulation targets based on anatomical landmarks rather than individual brain connectivity. These standardized approaches are easier for insurers to evaluate because they follow fixed treatment models.
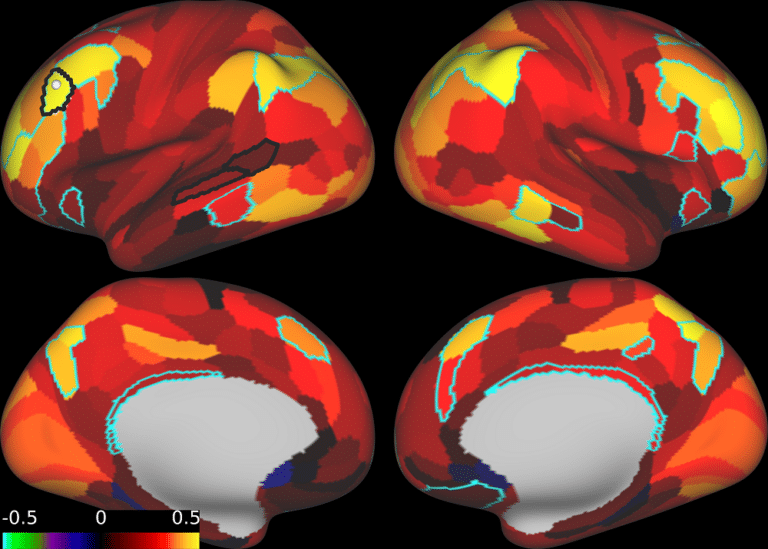
At Neurotherapeutix, treatment is delivered using fMRI-guided TMS therapy, informed by functional MRI–based computational brain mapping. This approach allows clinicians to tailor stimulation targets to each individual’s unique brain connectivity patterns, supporting a more personalized treatment plan across a wide range of mental health and neurological conditions.
Because fMRI-guided TMS therapy represents an advanced, precision-based methodology, it is not typically included within standard insurance reimbursement frameworks. As a result, coverage decisions may vary based on treatment technology and clinical approach rather than patient need alone.
What if TMS isn’t covered?
If insurance does not cover TMS therapy, there may still be options to consider.
Out-of-network reimbursement
Some patients choose to pursue treatment and submit claims independently to their insurance provider for possible reimbursement. Outcomes vary by plan, and reimbursement is not guaranteed.
Our team can help explain what documentation may be needed if you choose to explore this option.
Paying out of pocket
When insurance coverage is not available, fMRI-guided TMS therapy at Neurotherapeutix is offered as a self-pay service. This allows treatment decisions to be guided by clinical goals rather than insurance requirements.
Financial considerations are discussed directly with our team so patients can evaluate options thoughtfully and without pressure.
How Neurotherapeutix helps with insurance questions
Navigating insurance decisions can feel overwhelming, especially when you’re already focused on your health or supporting a loved one.
At Neurotherapeutix, we help patients:
- Understand how insurance coverage for TMS is typically evaluated
- Clarify why coverage varies across clinics and technologies
- Explore financial considerations transparently
- Make informed decisions without pressure or obligation
While insurance policies are outside our control, our goal is to provide clarity and guidance so you can decide what feels right for you.
Exploring next steps with confidence
Insurance coverage is only one part of the decision-making process.
For many patients, clearly understanding their options and feeling supported throughout the process are just as important.
If you have questions about TMS therapy at Neurotherapeutix or want help navigating insurance considerations, you can request an appointment to speak with our team and explore next steps together.
FAQs About TMS Insurance Coverage
Is TMS therapy usually covered by insurance?
Sometimes. Coverage depends on diagnosis, treatment history, insurance provider, and how the therapy is delivered. Approval is not guaranteed.
Does Medicare cover TMS therapy?
Medicare may provide coverage under specific circumstances when medical necessity criteria are met. Coverage details vary and should be confirmed directly with Medicare.
Will insurance cover fMRI-guided TMS?
Most insurance policies are written around standard TMS protocols. Advanced imaging-guided approaches are not typically included in coverage frameworks.
What if my insurance denies TMS treatment?
If coverage is denied, you may still explore options such as out-of-network reimbursement or self-pay treatment. Our team can help explain potential next steps.
Can I get reimbursed if I pay out of pocket for TMS?
Some insurance plans allow patients to submit claims independently for possible reimbursement. Approval depends on individual plan benefits and is not guaranteed.